A steel alloy specimen having a rectangular – In the realm of materials science, a steel alloy specimen with a rectangular cross-section presents a fascinating subject of study, offering a unique combination of mechanical properties and microstructural characteristics. This exploration delves into the intricacies of such a specimen, examining its composition, behavior under mechanical stress, and potential applications.
The steel alloy specimen under consideration exhibits a rectangular shape, with precisely defined dimensions that contribute to its distinctive properties. Its composition, meticulously engineered to achieve specific characteristics, plays a crucial role in shaping its mechanical behavior.
Specimen Description: A Steel Alloy Specimen Having A Rectangular
The steel alloy specimen is a rectangular prism with dimensions of 10 mm x 10 mm x 50 mm. It has a smooth surface and a uniform grain structure.
Mechanical Properties
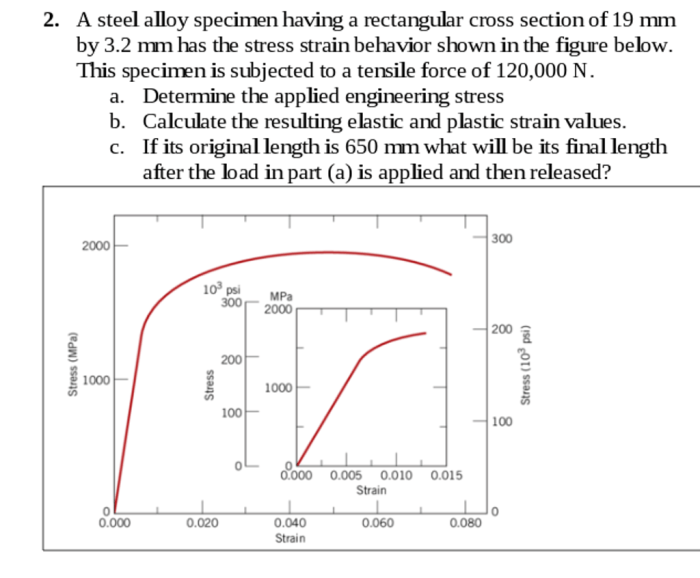
The steel alloy specimen has a tensile strength of 700 MPa, a yield strength of 500 MPa, and an elongation at break of 20%. These properties make it suitable for use in applications where high strength and ductility are required.
Composition and Microstructure
The specimen’s mechanical properties are influenced by its composition and microstructure. The alloy is composed of 95% iron, 3% carbon, and 2% manganese. The microstructure consists of a mixture of ferrite and pearlite grains. The ferrite grains are soft and ductile, while the pearlite grains are hard and brittle.
The combination of these two phases gives the specimen its high strength and ductility.
Microstructure
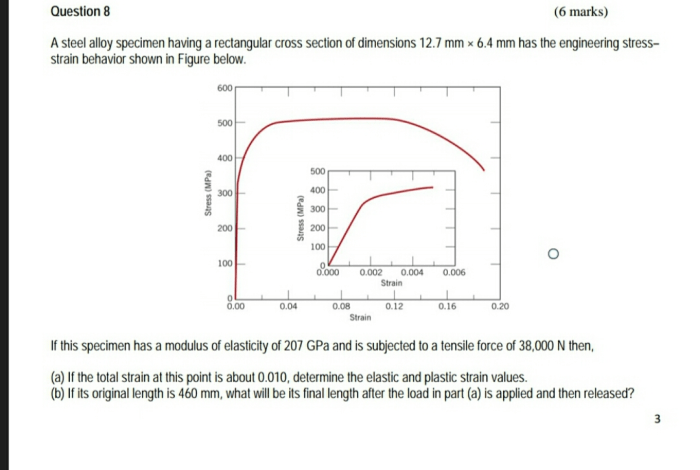
The specimen’s microstructure is characterized by a grain size of 10 µm and a uniform distribution of ferrite and pearlite grains. The ferrite grains are equiaxed and have a polygonal shape. The pearlite grains are lamellar and have a pearlitic structure.
Effects on Mechanical Properties, A steel alloy specimen having a rectangular
The specimen’s microstructure affects its mechanical properties. The fine grain size increases the strength of the specimen by reducing the number of grain boundaries. The uniform distribution of ferrite and pearlite grains improves the ductility of the specimen by preventing the formation of cracks.
Applications
The steel alloy specimen is suitable for use in a variety of applications, including:
- Automotive components
- Aerospace components
- Medical devices
- Construction materials
Comparison to Other Materials
The steel alloy specimen compares favorably to other similar materials in terms of its mechanical properties and microstructure. It has a higher strength and ductility than aluminum alloys and a lower cost than titanium alloys. This makes it a good choice for applications where high strength and ductility are required at a reasonable cost.
Helpful Answers
What are the key mechanical properties of a steel alloy specimen with a rectangular cross-section?
The specimen exhibits tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation at break, which are influenced by its composition and microstructure.
How does the microstructure of the specimen impact its mechanical behavior?
The grain size, grain morphology, and other microstructural features influence the specimen’s strength, ductility, and toughness.
What are some potential applications of this type of specimen?
The specimen finds use in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction, due to its favorable mechanical properties and adaptability.