The decline of feudalism answer key offers a comprehensive understanding of the complex historical process that transformed medieval Europe. This guide delves into the multifaceted factors that contributed to the decline of feudalism, exploring socio-economic, political, cultural, and military developments, as well as regional variations.
The decline of feudalism marked a significant turning point in European history, paving the way for the rise of nation-states, capitalism, and the modern world.
Socio-Economic Factors
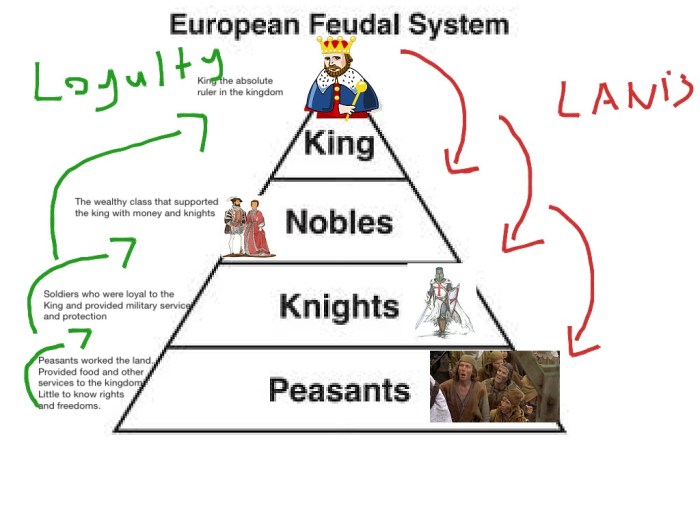
The decline of feudalism was accompanied by significant socio-economic transformations. These factors contributed to the gradual erosion of feudal structures and the emergence of new economic and social relationships.
A fundamental shift occurred from agrarian to mercantile economies. Agricultural production, which had been the mainstay of feudal society, gradually gave way to trade and commerce. This transition was driven by several factors, including technological advancements in transportation and communication, as well as the rise of urban centers.
Decline of Serfdom and Rise of Free Labor
The feudal system was characterized by serfdom, a form of labor in which peasants were bound to the land and owed obligations to their lord. However, over time, the institution of serfdom began to decline. Several factors contributed to this process, including the growth of trade and the demand for labor in urban areas.
As serfs gained economic independence, they were able to negotiate for better terms or even break free from their feudal obligations.
Emergence of Urban Centers and Growth of Trade
The rise of urban centers played a crucial role in the decline of feudalism. Cities became hubs of trade and commerce, attracting merchants, artisans, and other skilled workers. The growth of urban centers created new opportunities for economic mobility and social advancement, undermining the traditional feudal hierarchy.
The expansion of trade further contributed to the decline of feudalism. Long-distance trade routes connected different regions and facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas. This led to the rise of merchant guilds and other commercial organizations, which challenged the economic dominance of the feudal nobility.
Political Developments: The Decline Of Feudalism Answer Key

The feudal system began to decline in the late Middle Ages due to several political developments. One major factor was the weakening of feudal lords and the rise of centralized monarchies. As kings gained more power, they began to challenge the authority of the feudal lords.
They also began to create their own armies, which made them less dependent on the feudal lords for military support.Another factor that contributed to the decline of feudalism was the Hundred Years’ War. This war, which lasted from 1337 to 1453, devastated much of Europe.
It led to the deaths of many feudal lords and the destruction of many castles. The war also weakened the power of the feudal lords, as they were unable to protect their lands from attack.The Black Death also played a role in the decline of feudalism.
This plague, which struck Europe in the mid-14th century, killed an estimated 30-60% of the population. The Black Death caused a severe labor shortage, which led to an increase in wages for peasants. This made it more difficult for feudal lords to maintain their control over the peasantry.Finally,
the development of representative assemblies also contributed to the decline of feudalism. These assemblies, which were made up of representatives from different social classes, began to challenge the authority of the feudal lords. They also began to pass laws that limited the power of the feudal lords.As
a result of these political developments, the feudal system began to decline in the late Middle Ages. By the end of the 15th century, it had been replaced by a new system of government based on centralized monarchies and representative assemblies.
The Weakening of Feudal Lords
The feudal system was based on the power of feudal lords. These lords owned land and had the right to collect taxes from the peasants who lived on their land. They also had the right to raise armies and to administer justice.
However, the power of feudal lords began to decline in the late Middle Ages.One reason for the decline of feudal lords was the rise of centralized monarchies. As kings gained more power, they began to challenge the authority of the feudal lords.
They also began to create their own armies, which made them less dependent on the feudal lords for military support.Another reason for the decline of feudal lords was the Hundred Years’ War. This war, which lasted from 1337 to 1453, devastated much of Europe.
It led to the deaths of many feudal lords and the destruction of many castles. The war also weakened the power of the feudal lords, as they were unable to protect their lands from attack.Finally, the Black Death also played a role in the decline of feudal lords.
This plague, which struck Europe in the mid-14th century, killed an estimated 30-60% of the population. The Black Death caused a severe labor shortage, which led to an increase in wages for peasants. This made it more difficult for feudal lords to maintain their control over the peasantry.
The Rise of Centralized Monarchies
As the power of feudal lords declined, the power of centralized monarchies increased. Kings began to gain more control over their kingdoms. They also began to create their own armies and to administer justice.One of the most important factors in the rise of centralized monarchies was the development of new technologies.
These technologies, such as gunpowder and printing, made it easier for kings to control their kingdoms. Gunpowder made it possible for kings to defeat feudal lords in battle. Printing made it possible for kings to spread their ideas and propaganda throughout their kingdoms.Another
factor that contributed to the rise of centralized monarchies was the growth of trade and commerce. As trade and commerce grew, kings began to collect more taxes. This gave them the resources they needed to create their own armies and to administer justice.Finally,
the Hundred Years’ War also played a role in the rise of centralized monarchies. This war weakened the power of feudal lords and made it easier for kings to gain control over their kingdoms.
The Development of Representative Assemblies, The decline of feudalism answer key
Another important factor in the decline of feudalism was the development of representative assemblies. These assemblies, which were made up of representatives from different social classes, began to challenge the authority of the feudal lords. They also began to pass laws that limited the power of the feudal lords.One
of the most important representative assemblies was the English Parliament. The Parliament was first established in the 13th century. It was made up of representatives from the nobility, the clergy, and the common people. The Parliament began to pass laws that limited the power of the king.
It also began to hold the king accountable for his actions.Other representative assemblies were also established in Europe during the late Middle Ages. These assemblies, such as the French Estates-General and the Spanish Cortes, also began to challenge the authority of the feudal lords.
They also began to pass laws that limited the power of the feudal lords.The development of representative assemblies was a major factor in the decline of feudalism. These assemblies gave the people a voice in government. They also helped to limit the power of the feudal lords.
Cultural and Intellectual Changes

The decline of feudalism was influenced by significant cultural and intellectual changes that challenged the established feudal values and societal norms. These changes included the rise of humanism, the Renaissance, the spread of new ideas facilitated by the printing press, and the growing emphasis on individualism and the decline of religious authority.
Influence of Humanism and the Renaissance on Feudal Values
Humanism, a philosophical and literary movement that emerged in the 14th century, emphasized the importance of human reason, individuality, and secular concerns. This challenged the dominant religious worldview of the Middle Ages, which emphasized the importance of divine authority and the afterlife.
The Renaissance, a cultural movement that followed humanism, further promoted the study of classical literature, art, and science, leading to a renewed interest in the human experience and the pursuit of knowledge. These movements weakened the hold of feudal values, which emphasized hierarchy, obedience, and the importance of tradition.
Impact of the Printing Press and the Spread of New Ideas
The invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the mid-15th century revolutionized the dissemination of information. Before the printing press, books were handwritten and expensive, limiting access to knowledge to a privileged few. With the printing press, books became more widely available and affordable, leading to a rapid spread of new ideas and the growth of literacy.
This contributed to the decline of feudalism by undermining the authority of the Church and the nobility, who had previously controlled the flow of information.
Rise of Individualism and the Decline of Religious Authority
The rise of humanism and the Renaissance also led to a growing emphasis on individualism and the importance of personal experience and expression. This challenged the collectivist values of feudal society, which emphasized the importance of family, community, and the lord-vassal relationship.
Additionally, the Reformation, a religious movement that began in the early 16th century, challenged the authority of the Catholic Church and led to the rise of Protestantism. This further weakened the hold of religious authority in feudal society, contributing to the decline of feudalism.
Military Innovations

The decline of feudalism was partly driven by military innovations that challenged the traditional feudal system and its reliance on armored knights and levies.
One significant development was the introduction of gunpowder into warfare. The invention of gunpowder-powered weapons like cannons and firearms revolutionized warfare, rendering traditional fortifications and armor obsolete. Cannons could breach castle walls, and firearms allowed infantry to defeat heavily armored knights.
Rise of Professional Armies
The effectiveness of gunpowder weapons led to the rise of professional armies. Feudal levies, composed of poorly trained and equipped peasants, proved ineffective against professional soldiers with specialized training and advanced weaponry. Kings and lords began to raise standing armies of professional soldiers, who were paid and trained to fight full-time.
Decline of Feudal Levies
As professional armies grew in strength and effectiveness, the role of feudal levies declined. Knights became less important on the battlefield, and the feudal obligation to provide military service gradually diminished. This shift weakened the feudal system’s military foundation and contributed to its decline.
Changing Role of Castles and Fortifications
The introduction of gunpowder also transformed the role of castles and fortifications. Traditional castles, designed to withstand medieval siege weapons, became vulnerable to cannon fire. As a result, castles lost their military significance and were increasingly used as residences or administrative centers.
Regional Variations

The decline of feudalism was not a uniform process across Europe. It occurred at different paces and to varying degrees in different regions, influenced by a range of unique factors. This table compares the decline of feudalism in several key regions of Europe, highlighting the unique factors that shaped its course and the impact it had on the political, social, and economic landscape.
| Region | Unique Factors | Pace and Extent of Decline | Political, Social, and Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| England | – Strong central monarchy
|
– Early and rapid decline of feudalism
|
|
| France | – Weaker central monarchy
|
– Gradual decline of feudalism over a longer period
|
|
| Germany | – Fragmented political landscape
|
– Slow and uneven decline of feudalism
|
|
| Italy | – Highly urbanized
|
– Early decline of feudalism in urban areas
|
|
| Spain | – Reconquista against the Moors
|
– Gradual decline of feudalism over a long period
|
Detailed FAQs
What were the key socio-economic factors that contributed to the decline of feudalism?
The shift from agrarian to mercantile economies, the decline of serfdom and the rise of free labor, and the emergence of urban centers and the growth of trade played significant roles.
How did political developments impact the decline of feudalism?
The weakening of feudal lords, the rise of centralized monarchies, the impact of the Hundred Years’ War and the Black Death, and the development of representative assemblies contributed to the decline of feudal structures.
What were the cultural and intellectual changes that influenced the decline of feudalism?
The influence of humanism and the Renaissance, the impact of the printing press and the spread of new ideas, and the rise of individualism and the decline of religious authority played significant roles.
How did military innovations contribute to the decline of feudalism?
The development of gunpowder and its impact on warfare, the rise of professional armies and the decline of feudal levies, and the changing role of castles and fortifications played significant roles.
Were there regional variations in the decline of feudalism?
Yes, the pace and extent of feudal decline varied across different regions of Europe due to unique factors such as geography, political structures, and economic conditions.
